TN vs IPS vs VA: what they are, differences and how to choose
When selecting a display for your embedded system or industrial application, choosing the right panel technology is crucial. TN, IPS, and VA are three of the most common types of LCD panels, each with its own advantages and trade-offs.
Keep reading to understand these differences and make an informed decision for your project.
 Selecting the right display technology involves evaluating key factors like performance, visual quality, and cost. Below are the most important aspects to consider:
Selecting the right display technology involves evaluating key factors like performance, visual quality, and cost. Below are the most important aspects to consider:
TN vs IPS vs VA: what are they?
TN (Twisted Nematic), IPS (In-Plane Switching), and VA (Vertical Alignment) are three types of LCD panel technologies that define how liquid crystals align to produce images. Each has unique characteristics in terms of speed, color accuracy, viewing angles, and cost, making them suitable for different applications. Explore more each one in the topics bellow:Twisted Nematic (TN)
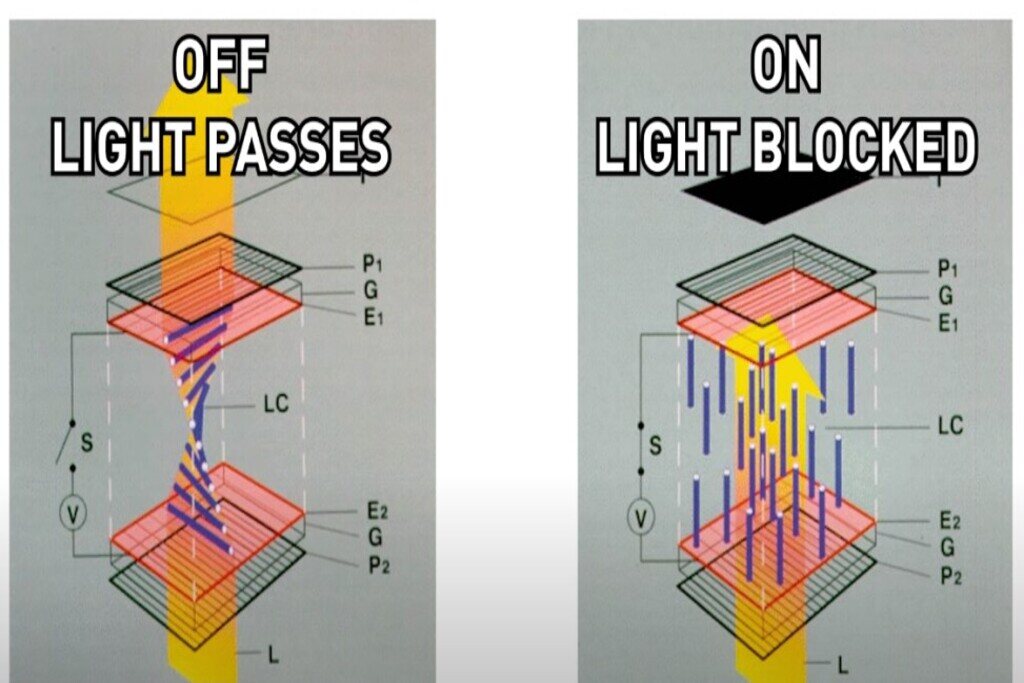
It stands for Twisted Nematic Phase and is the oldest technology in LCD technology. This refers to the Twisted Nematic Effect, which allows liquid crystal molecules to be voltage-controlled. The TN effect is used to change the orientation of the liquid crystal when a voltage is applied. In the absence of voltage, the crystal molecules would twist 90 degrees to allow light to pass through. Then, when a voltage is applied, these crystals are essentially undistorted and bind to a layer of polarization, preventing light from passing through.
In Plane Switching (IPS)
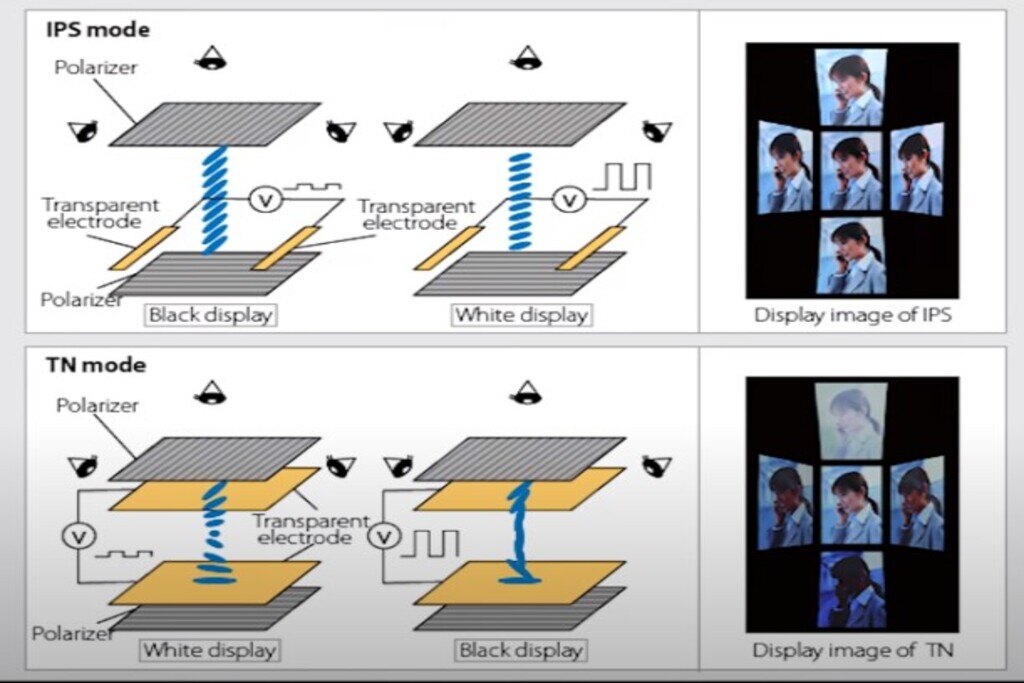
IPS stands for in-plane switching. Like all liquid crystal displays, it also uses voltage to control the arrangement of liquid crystals. However, unlike TN, IPS liquid crystal uses a different crystal orientation, where the crystal is parallel to the glass substrate. In other words, instead of “twisting” the crystal to change the amount of light passing through, the IPS crystal is essentially rotating, which has many advantages.
Vertical Alignment (VA)
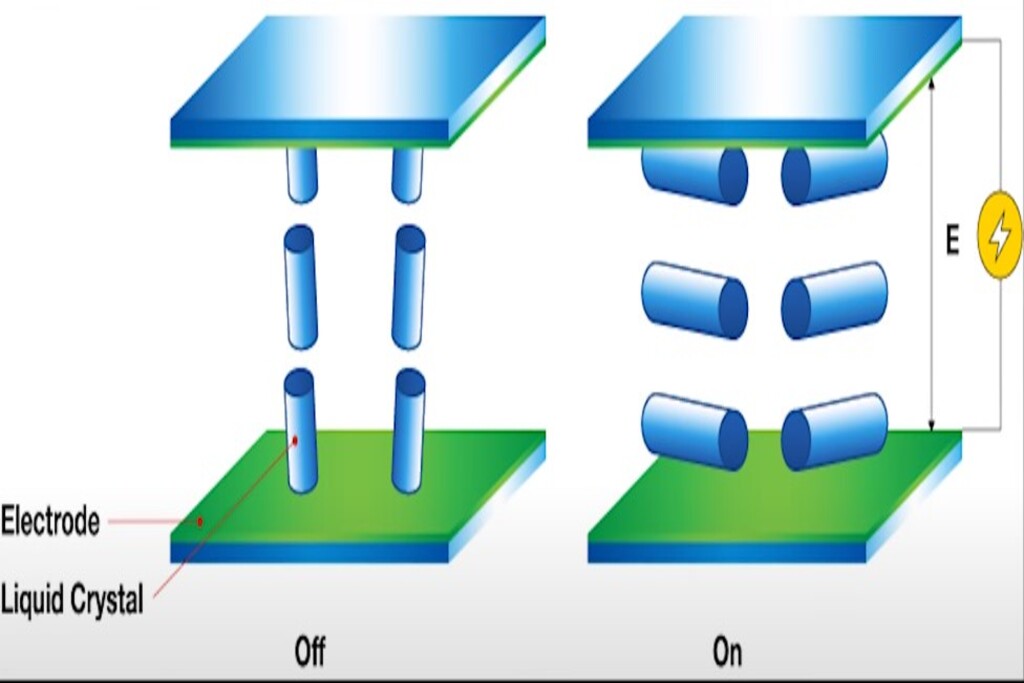
VA stands for Vertical Alignment, and as the name suggests, this technology uses vertically aligned liquid crystals that tilt when a voltage is applied to send light through, a key difference between IPS and VA. With VA, the crystals are perpendicular to the substrate, while with IPS, the crystals are parallel.
TN vs IPS vs VA: what is the difference?
While all three technologies are used in modern displays, they differ significantly in key aspects such as response time, color accuracy, viewing angles, and contrast. Read more about the differences between them next:Viewing angles
The TN panel has the weakest viewing angle, with significant changes in color and contrast in the horizontal (and especially vertical) direction. Typically, the viewing Angle is rated at 170/160, but in practice, you’ll get a very bad offset when viewing anywhere but dead spots. Overall, this is a big weakness for TN. Both the VA and IPS panels are significantly better, with the IPS having the best viewing angle. The 178/178 view level is a true reflection of the IPS, and you won’t get much color change or contrast from any angle. In this respect, VA performed less well than IPS, mainly due to the contrast offset at the eccentric angle. Because the VA (especially the TN) has some color and contrast deviation when tilted to view, they are not as suitable for color-intensive professional work as the IPS panels, which is why you see most professional-grade displays with IPS.Brightness & contrast ratios
In terms of brightness, there is not much difference between the three technologies because the backlight that determines brightness is separate from the LCD panel. However, there is a significant difference in contrast. TN and IPS panels typically have a contrast ratio of 1000:1. TN panels usually have the lowest contrast, with entry-level panels ranging from 700:1 to 900:1 and good panels reaching 1000:1. The range of IPS is wider, with some as low as 700:1, but some desktop monitors and some laptop-level monitors that use IPS have the upper limit as high as 1500:1. For the VA panel, the best one can exceed 4500:1 easily. VA LCD display provides a far darker screen than TN & IPS. That is why they are used in the vehicle dashboard.Color quality
Color quality is another important difference between TN displays and other display panels. Color quality can be divided into two categories: color depth and gamut. On both counts, the TN panel is at a disadvantage. Many TN displays, especially entry-level models, are native to only 6 bits and use frame rate control (also known as FRC) to achieve standard 8-bit output. The 6-bit panel is prone to color ribbons, while the native 8-bit panel has a smoother color gradient and therefore better color output. For IPS and VA panels, you can still find 6-bit entry-level LCDs. But most of them are 8-bit. IPS technology can provide native 10-bit color. For color gamut, this is also an area where VA and IPS provide a superior experience. The best TN panels tend to be restricted sRGB. VA panels usually start with full sRGB coverage and reach about 90% DCI-P3 coverage. Using the IPS LCD panel, you can find the best panel with full DCI-P3 and Adobe RGB coverage. This is why you see most professional-grade LCD displays using IPS panels.Speed
TN panels are the fastest in terms of response time, making them a popular choice for applications that require quick refresh rates and minimal motion blur. IPS panels, while slightly slower, offer better color reproduction. VA panels strike a balance but often have slower response times than TN.TN or IPS or VA: what are the applications? Which is better?
Each panel type — TN, IPS, and VA — excels in different applications based on their unique strengths and limitations. Know more:- TN (Twisted Nematic): due to their fast response times and high refresh rates, TN panels are commonly used in applications that require real-time image updates, such as gaming monitors, industrial control interfaces, and low-cost embedded systems. However, they have poor color accuracy and limited viewing angles, making them less ideal for applications where visual clarity is a priority;
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): IPS panels deliver superior color accuracy and wide viewing angles, making them the preferred choice for applications that require detailed and vibrant visuals. This includes medical imaging, design and development interfaces, and high-end industrial touchscreen systems. While IPS displays generally have slower response times than TN, modern improvements have reduced this gap significantly;
- VA (Vertical Alignment): VA panels offer the best contrast ratios, making them excellent for applications where deep blacks and high contrast are necessary, such as in video displays, automotive dashboards, and medical diagnostics. They provide a good balance between TN and IPS, but their response times tend to be slower than TN panels.
TN or IPS or VA: how to choose for your project?
 Selecting the right display technology involves evaluating key factors like performance, visual quality, and cost. Below are the most important aspects to consider:
Selecting the right display technology involves evaluating key factors like performance, visual quality, and cost. Below are the most important aspects to consider:
Consider your primary use case
Your project’s purpose should be the primary deciding factor. If your application involves fast-moving visuals or requires minimal input lag, TN is the best fit. If color accuracy and a rich viewing experience are essential, IPS is the ideal choice. VA should be considered for applications requiring deep contrast and high-definition visuals, such as multimedia or medical imaging systems.Understand the color accuracy and viewing angles of the screens
For applications where precise color reproduction is crucial, such as medical monitors, industrial control panels, and multimedia interfaces, IPS displays are superior due to their accurate color representation and consistent visuals across wide viewing angles. TN panels, in contrast, suffer from color shifting when viewed from different angles, making them less suitable for collaborative or multi-user environments. VA panels offer better color accuracy than TN but still fall short of IPS in terms of consistency and vibrancy.Consider the screen size and resolution
Depending on your project, screen size and resolution can play a significant role. For applications requiring detailed data visualization, high-resolution IPS or VA displays provide better clarity. If cost and performance efficiency are key considerations, TN panels offer lower-resolution options at a more affordable price. Additionally, for space-constrained embedded systems, compact TFT LCD modules provide an excellent balance of performance and efficiency.Check the refresh rate and response time
If your project demands high-speed responsiveness, such as in gaming, interactive kiosks, or real-time monitoring systems, a higher refresh rate and lower response time are essential. TN panels are the fastest in this regard, making them ideal for high-motion applications. IPS and VA panels have improved in response times over the years, with some modern models coming close to TN in performance. However, VA panels still tend to have slower response times, leading to potential ghosting effects in fast-paced visuals.Think about your budget
Budget constraints will always be a factor when selecting a display. TN panels are the most cost-effective and widely available, making them a solid choice for budget-conscious projects that prioritize performance over visual quality. IPS panels, while more expensive, provide excellent color reproduction and are ideal for applications where image clarity is a priority. VA panels typically fall in the mid-to-high price range, offering good contrast and color depth at a reasonable cost.Count on Proculus’s help for your project
Choosing the right display module can be complex, but Proculus Technologies is here to help. Our UART TFT LCD modules simplify development by providing high-performance, easy-to-integrate display solutions tailored for industrial and embedded applications. Whether you need a fast TN panel for responsive interfaces, a high-quality IPS display for professional-grade visuals, or a contrast-rich VA screen for optimal clarity, we have the right solution for your needs. Explore our UART TFT LCD modules and discover how Proculus can enhance your project with innovative display solutions.Conclusion
When deciding between TN, IPS, or VA panels, it’s essential to evaluate speed, color accuracy, contrast, viewing angles, and budget considerations. Each panel type serves different applications, and choosing the right one depends on your project’s specific needs. By carefully assessing these factors and leveraging Proculus Technologies’ experienced integration specialists, you can ensure a high-quality, optimized display solution for your embedded system.
Category:
Author:
Client:
Date:
PHP Code Snippets Powered By : XYZScripts.com
 English
English


